Nowadays, everything designers create seems more desirable due to its uniqueness and exceptionality. Therefore, it should not be surprising that the essence of the term "design" as innovative, exceptional, and unrepeatable has also crept into the IT world.
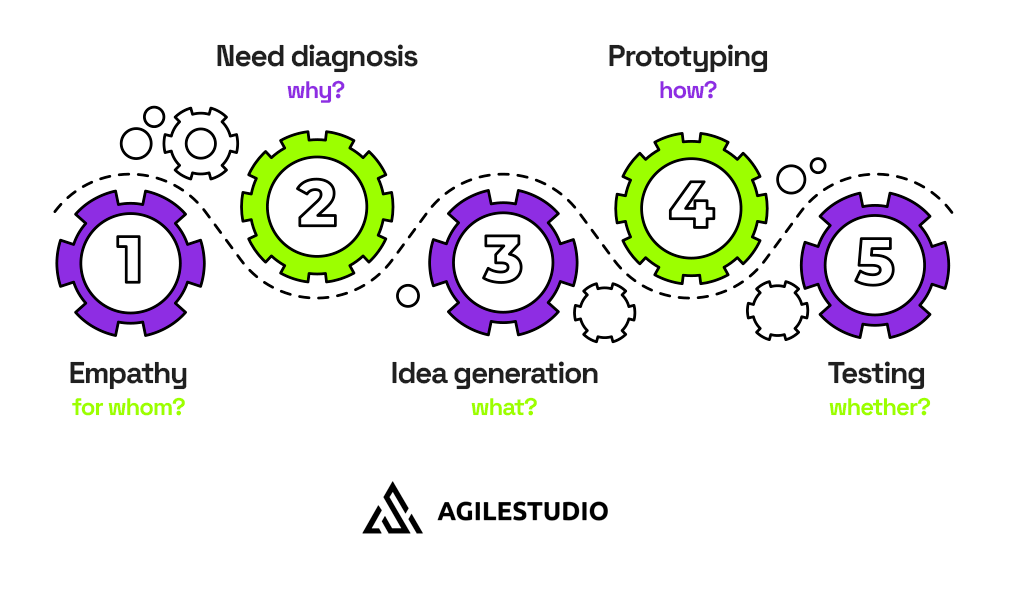
Design Thinking has become a method of creating innovative products and services that meet customer needs. It allows you to quickly and effectively respond to changes in user behavior and their problems. By undertaking and committing to the 5-step process (empathy, diagnosis of needs, generating ideas, prototyping, and testing), you will quickly and effectively increase the chances of taking care of customers' real needs.
When technology meets creative thinking
The term "Design Thinking" had already appeared in the 1960s, but at first, it mainly concerned designers and architects who creatively designed objects or buildings. It was not until the 21st century that it began to be used as a formalized term for solving problems - Design Thinking.
The breakthrough moment of popularization of the term in the business and IT industry was marked by the research at Stanford University, conducted by David Kelly, co-founder of IDEO. The research aimed to understand the creative process of creating products that are the most successful. The main factor of success turned out to be a practical approach to solving problems combined with a focus on the users, their needs, demographics, and main characteristics.
Thanks to the universality of the approach and its combination with technology, Design Thinking gained popularity in companies such as IBM, SAP, Samsung, and Raiffeisen. Nowadays, it is appreciated mainly for non-standard thinking "outside-the-box", cooperation of many departments, and focus on innovation, focusing on the needs of the customer.
5 steps to meet user expectations
Design Thinking as a problem-solving process focuses on 5 steps that address specific questions:
- Empathy - for whom?
- Need diagnosis - why?
- Idea generation - what?
- Prototyping - how?
- Testing - whether?
An important advantage of the method is its universality and speed, which we owe to the iterative and non-linear approach. This means that we close each step as quickly as possible, making full use of the time devoted, and if necessary, we can return to any step, to collect new information.
However, it is important to remember to maintain full objectivity. We can’t allow ourselves to express our own opinions or let our internal assumptions come to lead at any stage. We must approach the entire process with openness and the desire to gain new knowledge, even if it is the opposite of what we have assumed. zyskania nowej wiedzy, nawet jeśli jest przeciwna w stosunku do tego, co zakładaliśmy.
Empathy, who we are creating the solution for
To create solutions focused on the user, the most important thing is to fully understand them. In the first step of the process, our task is to get to know the needs, behaviors, and problems of our customers or users as best as we can, e.g., empathize with them. We must "step into their shoes" to understand their perspective. The most important are conversations, and interviews, during which we will listen and observe real needs.
We can do this by using the following techniques:
- ⇾ Involve the user directly: prepare questions for the interview and conduct it with real users.
Tip!
- ⇾ Use only open-ended questions to get as much information as possible (start with questions like: how, why, when, and in what way)
- ⇾ Avoid closed-ended questions starting with ‘Do?’
- ⇾ Try not to impose a solution or your beliefs, e.g. instead of asking “How important is it for you to spend your free time actively?” ask “How do you like to spend your free time?”.
- ⇾ Observe the user’s behavior: try to learn about the user’s behavior in their environment, create a map of the activities they perform, write down quotes, and take notes that describe the user’s experience.
Tip!
- ⇾ Become an invisible observer so that the user feels as comfortable as possible.
- ⇾ In this technique, do not ask questions, leave them for the interview.
- ⇾ Become the user: try to enter or recreate the user’s environment, and allow yourself to experience the same emotions as the user.
Tip!
- ⇾ You have to become an actor who completely steps into the shoes of the user, allow yourself to retain your prejudices or experiences.
- ⇾ Think about what you feel at the moment, what is difficult for you, and what is easy for you.
The Empathy step is crucial for the success of the entire method, which is why it can take up to 40-50% of the time.
Needs diagnosis, or defining problems
In the second step, we ask ourselves the question "Why?" does the client or user feel a certain way. We try to find the root cause of the problem and understand why we want to solve this problem.
The diagnosis of the problem must be based on the analysis of the information we have collected during the Empathy step. Our task is to rely solely on collected insights, we cannot add or interpret words. We must remain fully objective at all times. If a given behavior is still incomprehensible, or if we have gaps in our notes, let's go back to step one. Otherwise, we risk addressing the wrong problem.
A well-defined problem should:
- Reflect the emotions and needs of our users.
- Use explicit language to emphasize the message.
- Use simple and understandable vocabulary.
- Create numerous possibilities for solving the problem.
- Contain important information.
Tip!
- ⇾ Do not enter the solution to your problem.
- ⇾ Try to describe the specific problem (do not go too broadly and universally).
Generating ideas, how we want to solve the user's problem
Generating ideas is the first step when you and your team come to the fore. In the first two steps, our task is to listen and draw conclusions, but in the step of generating ideas, our creativity, cooperation, and the ability to think outside the box count.
Our task is to create as many ideas as possible (even crazy ones) that will help solve the user's problem. We use the diversity of the team and the ideas of each person participating in the workshops.
Tip!
- ⇾ Do not judge the ideas of others.
- ⇾ Do not discuss ideas, create as many as possible.
- ⇾ There are no stupid ideas, each can turn into a valuable solution.
- ⇾ You can use various techniques, such as brainstorming or mind mapping.
To help create a list of ideas, you can ask questions that will change the context and help us think outside the box:
- ⇾ How would someone else (dad, president, child) approach solving the problem?
- ⇾ What if our budget was unlimited?
- ⇾ What if we lost the budget?
- ⇾ What if we were on Mars?
After collecting all the ideas, you can enter the process of discussing and choosing the idea you want to focus on first.
Tip!
- ⇾ Be open to ideas created by others, let the group decide which idea we will test first.
- ⇾ If you have trouble making a decision, you can use Dot Voting (everyone gets 2-3 votes for ideas, the idea with the highest number of votes wins).

Prototyping, or implementing the idea
The goal of the Prototyping step is to create a model that will represent our solution - a prototype - as quickly and cheaply as possible. It is to visualize how the idea will be implemented in practice so that the user can test it and express their opinion.
A prototype can take various forms, such as:
- ⇾ a mockup,
- ⇾ a plan written on a board,
- ⇾ a scene (showing behavior).
Remember that prototyping has two tasks:
- We increase our knowledge about the solution: by implementing the idea into practice, it changes our thinking, what and how we create, and what functions our solution should fulfill.
- We implement the user in the creative process: our goal is to present the idea so that the user can feel, experience our solution, and express their opinion. In this way, we give them a real opportunity to influence the final effect.
Tip!
- ⇾ Try to create the cheapest and fastest solution possible, it doesn't have to be perfect, it should present a solution to the problem.
- ⇾ When creating a solution, go back to the problem and make sure that it addresses the problem posed.
Testing, or implementing the user into our solution
The last step, Testing, is primarily aimed at collecting feedback on our solution. We want to make sure that our thinking process is correct, and whether the proposed solution addresses the user's problem.
Testing is the moment when we show our prototype, discuss it, and observe the user's reaction. We collect their opinions and suggestions, which are intended to help us create the final product. We can test the prototype many times and in an iterative way to improve good ideas and reject unsuccessful ones as quickly as possible.
Tip!
- ⇾ During testing, do not argue with the user, listen and write down information, and only then you will gain full objectivity.
- ⇾ Use testing to gain additional information about the user, their behavior, and interactions with the proposed solution.
Don't be afraid if testing shows that the user doesn't like the solution! This is what Design Thinking is all about - to gain knowledge about the user and their problems as quickly as possible.

Summary
Design Thinking is a method of solving problems in which the user and their problems are the most important. As an approach, it is flexible and adapts to the context. It aims to create innovative solutions and address the real user needs.
It requires full objectivity, great creativity, and cooperation in the team and with the user. Our task is to act quickly, not to waste energy on solutions that will not meet the customer's needs.
In the Design Thinking process, we must allow ourselves to "fail", and gain knowledge that our initial solution is not what the user needed. Users, their needs, and problems are the most important.